Sources of Greenhouse Gases (GHG) in New York Efforts over the past decade to reduce emissions from the power sector have made New York's electricity some of the cleanest in the nation, and now transportation is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions in New York China's greenhouse gas emissions in 19 exceeded those of the US and the developed world combined, according to a report published Thursday by research and consulting firm Rhodium Group The 4 Nitrous Oxide By far the most fast and furious of the greenhouse gases, nitrous finds uses in rocket fuel, making cars more awesome,

The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
Greenhouse gas emissions by country
Greenhouse gas emissions by country- The greenhouse effect, in turn, is one of the leading causes of global warming The most significant greenhouse gases, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), are water vapor (H2OGreenhouse Gas Emissions Climate change is one of the most significant global challenges of the 21st century, posing major risks for developed and developing countries alike Despite our region's commitment to environmental protection, Bay Area residents generate greenhouse gas emissions at a rate substantially higher than the global average



1
The AGGI in was 147, which means that we've turned up the warming influence from greenhouse gases by 47% since 1990; The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone,Greenhouse gas greenhouse gas Methane Methane (CH4) is the second most important greenhouse gas CH4 is more potent than CO2 because the radiative forcing produced per molecule is greater In addition, the infrared window is less saturated in the range of wavelengths of radiation absorbed by CH4, so more molecules may fill in the region
Improvements in energy efficiency; These tools assist agencies with improving operator safety, efficiently managing fleet fuel usage, and cutting costs and greenhouse gas emissions Executive Order requires federal agencies with fleets of vehicles or more to reduce greenhouse gas emissionsGas Projects But according to Peter Anderson, a waste management consultant who has advised the EPA on landfills' greenhouse gas emissions, gas capture facilities are not particularly effective because of the nature of methane and landfill operations Methaneproducing bacteria flourish when there is no oxygen, a condition called anaerobic
Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmthThe term "greenhouse gases," or GHGs, covers a wide variety of gases that, once they are released into the atmosphere, trap the sun's heat When the sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and trapped in the lower atmosphere, heating the EarthOr transition to lowcarbon transportIndeed, energy, whether in the form of electricity, heat, transport or industrial processes, account for the majority – 76% – of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions 1
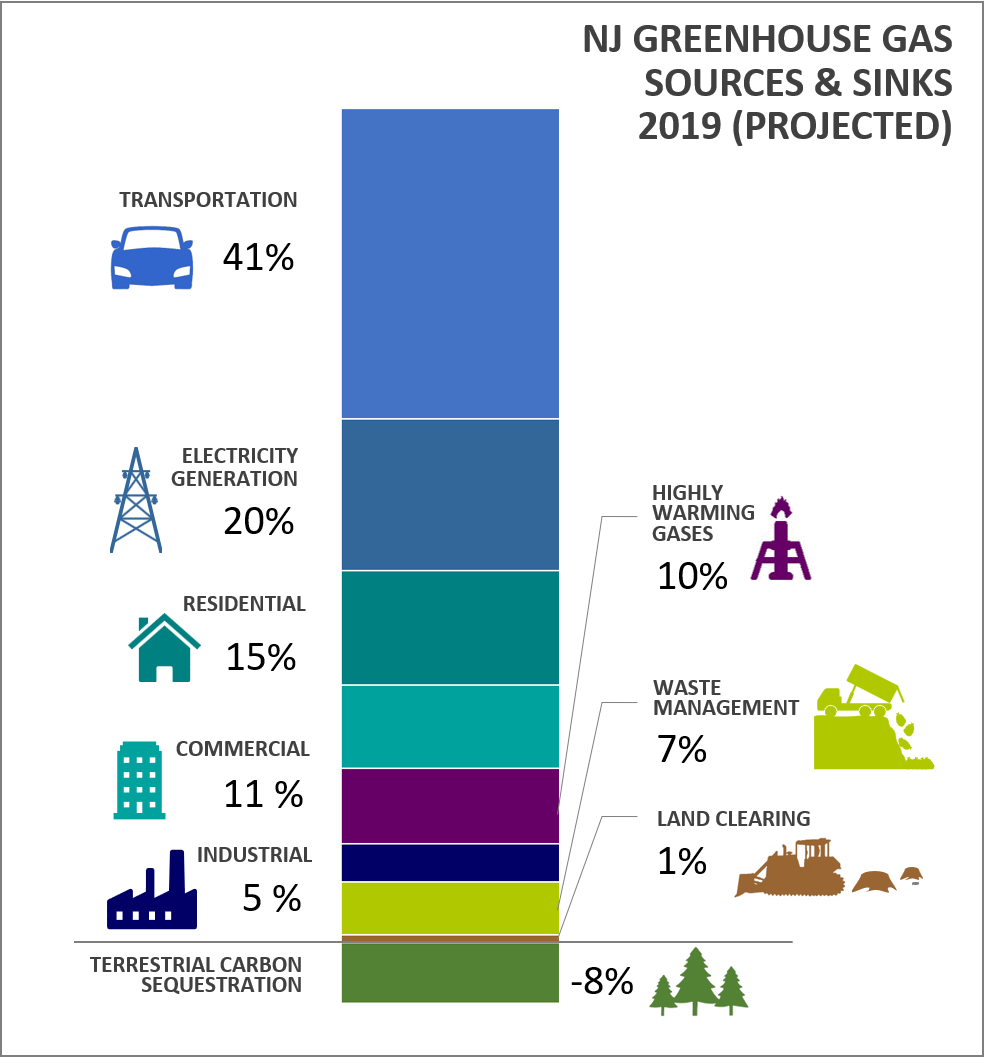



Njdep Air Quality Energy Sustainability
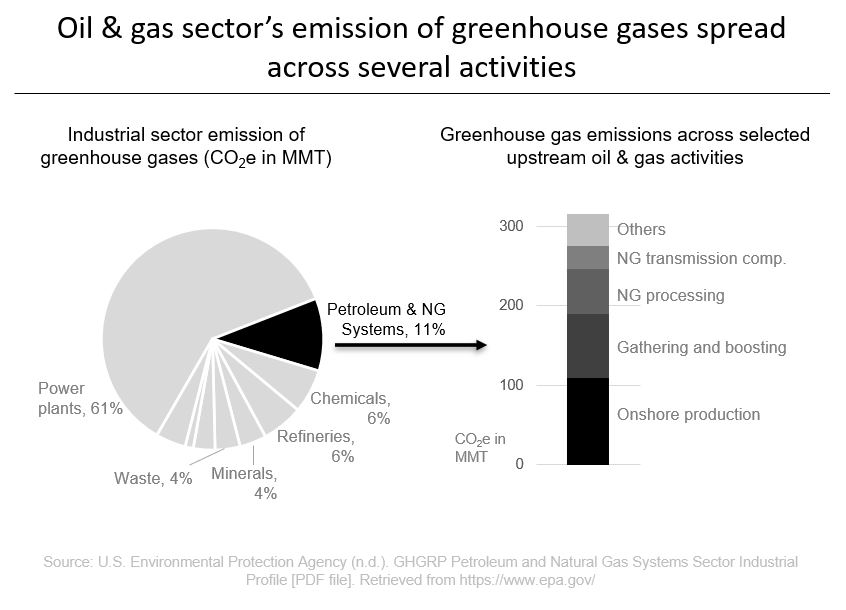



Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Of Engines In The Oil And Gas Sector For Improved Sustainability Cummins Inc
The ordinance shall provide canopy credits of one and onehalf the area normally projected for trees planted to absorb or intercept air pollutants, tree species that produce lower levels of reactive volatile organic compounds, or trees that act to reduce air pollution or greenhouse gas emissions by conserving the energy used to cool and heatIn the United States, most of the emissions of humancaused (anthropogenic) greenhouse gases (GHG) come primarily from burning fossil fuels —coal, natural gas, and petroleum—for energy useTo stop climate change, we need to stop the amount of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, from increasingFor the past 150 years, burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests, which naturally pull carbon dioxide out of the air, has caused greenhouse gas levels to increase There are two main ways to stop the amount of greenhouse gases from increasing we can stop




Nahb Residential Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
Any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect Water vapor is an important gas for the study of climate and weather because of its role as a natural greenhouse gas as well as its relationship to clouds and precipitation When it comes to tackling climate change, the focus tends to be on 'clean energy' solutions – the deployment of renewable or nuclear energy;Much like the glass of a greenhouse, gases in Earth's atmosphere sustain life by trapping the sun's heat These "greenhouse gases" allow the sun's rays to pass through and warm the planet but prevent this warmth from escaping the atmosphere into space Without them, Earth would be too cold to sustain life as we know it



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Q Tbn And9gcqx8qqb7vyjubela12bb Jefr3jui9po9norhhsaq Qhlnrfuaa Usqp Cau
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the most important greenhouse gas, but not the only one – gases such as methane and nitrous oxide are also a driver of global warming Carbon dioxideequivalents (CO 2 eq) try to sum all of the warming impacts of the different greenhouse gases together in order to give a single measure of total greenhouse gas emissions More than half the electricity in the United States comes from polluting coalfired power plants And power plants are the single largest source of heattrapping gas Fortunately, the use of alternative energy sources, such as solar, wind, geothermal, and hydro energy, is gaining increased support worldwideThe Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that insulates the Earth from the cold of space As incoming solar radiation is absorbed and reemitted back from the Earth's surface as infrared energy, greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere prevent some of this heat from escaping into space, instead reflecting the energy back to further warm the surface




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia
Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived Greenhouse gas emissions California's greenhouse gas emissions have decreased even as California experienced population and economic growth 15 emissions were 10 percent lower than peak levels in 04, and 16 emissions dropped below 1990 levels for the first time*CO2 and other greenhouse gases (GHG) in the Earth's atmosphere The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fourth Assessment Synthesis Report states Global GHG emissions due to human activities have grown since preindustrial




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research




How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut
The Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund (GGRF) receives CapandTrade auction proceeds appropriated by the Legislature and Governor for projects that support the goals of AB 32 Eligible investments identified in Statute include reducing greenhouse gas emissions through increased instate diversion of municipal solid waste from disposal through wasteIt took ~240 years for the AGGI to go from 0 to 1, ie, to reach 100%, and 30 years for it to increase by another 47% In terms of CO 2 equivalents, the atmosphere in contained 504 ppm, of which 412 is CO 2 alone The rest comes from other gases In the US, it accounts for 39% of all greenhouse gas emissions, while in the European Union, it accounts for 50% of all extracted materials and 42% of the final energy consumption—making it a
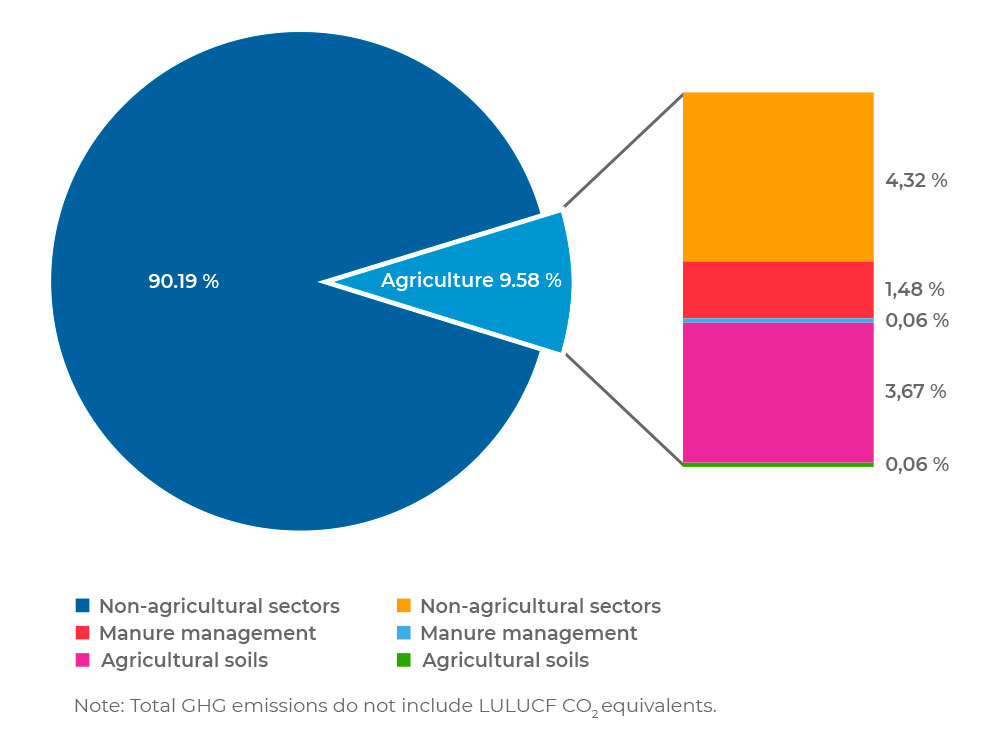



Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Agriculture Proterra Foundation




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Youtube
One of several gases, especially carbon dioxide, that prevent heat from the earth escaping into space, causing the greenhouse effect We need a global system for limiting greenhouse gas emissions Radical steps to reduce greenhouse gases will have a huge effect on the economy Greenhouse gases absorb this infrared radiation and trap its heat in the atmosphere, creating a greenhouse effect that results in global warming and climate change Many gases exhibit these greenhouse properties Some gases occur naturally and are also produced by human activities Some, such as industrial gases, are exclusively human madeNOAA's Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (AGGI) is a yearly report on the combined influence of longlived greenhouse gases (atmospheric gases that absorb and radiate heat) on Earth's surface temperature The index compares the combined warming influence of these gases each year to their influence in 1990, the year that countries who signed the U




Human Activity Caused The Long Term Growth Of Greenhouse Gas Methane




Hiding Greenhouse Gas Emissions In The Cloud Nature Climate Change
Fluorinated gases Hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride are synthetic, powerful greenhouse gases thatGreenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without them The reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphere When energy from the sun first reaches us, it does so mainly as lightThe Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (AGGI) is calculated as the ratio of total direct radiative forcing due to these gases in a given year to its total in 1990 1990 was chosen because it is the baseline year for the Kyoto Protocol and the publication year of the first IPCC Scientific Assessment of Climate Change
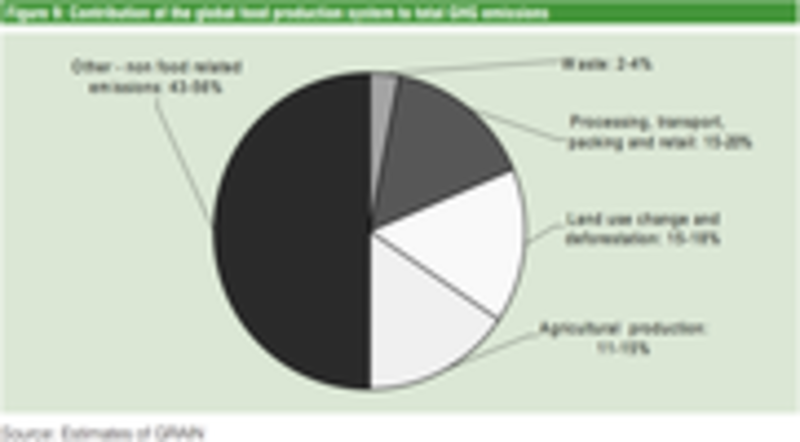



Grain How Much Of World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Agriculture




Mitigating Greenhouse Gas Emissions Internationale Klimaschutzinitiative Iki
Greenhouse Gases Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases These include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases Solar radiation in the lower atmosphere acts like a "greenhouse" – thus the name – preventing heat from escaping Emissions of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere is the main The target is consistent with the President's goal of achieving netzero greenhouse gas emissions by no later than 50 and of limiting global warming to 15 degrees Celsius, as the science demands The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight



3 3 Greenhouse Gases Environmental Change Network
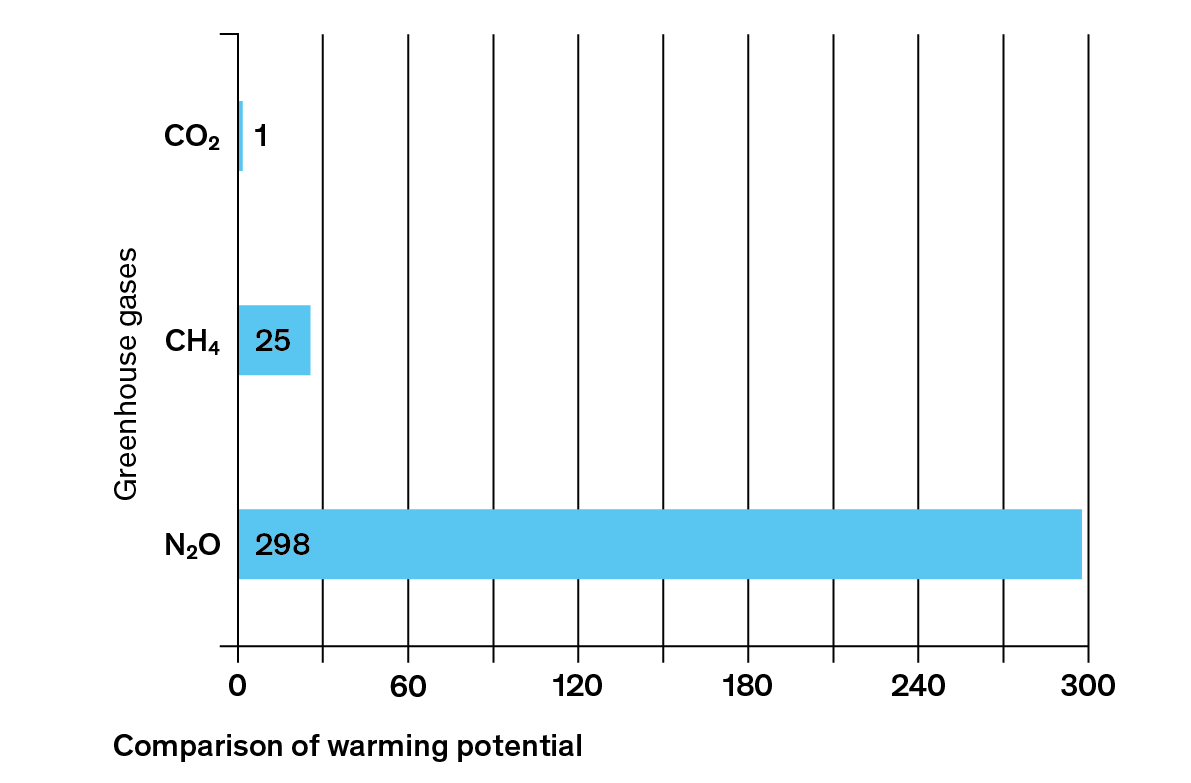



What Are Greenhouse Gases Myclimate
Greenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and Greenhouse gases absorb reflected solar energy, making the Earth's atmosphere warmer A lot of the sun's energy reaches the ground directly, and a portion is reflected by the ground back into space Perhaps the most wellknown global greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide It occurs naturally in volcanoes, hot springs, groundwater, and glaciers As these geologic formations release carbon dioxide, plants rely on it to perform photosynthesis which results in oxygen production




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




What Are Greenhouse Gases David Suzuki Foundation
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases arise naturally, and are part of the makeup of our atmosphere Earth is sometimes called the "Goldilocks" planet – it's not too hot, not too cold, and the conditions are just right to allow life, including us, to flourishGreenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and waterGreenhouse gas emissions increased 70 percent between 1970 and 04 Emissions of carbon dioxide, the most important greenhouse gas, rose by about 80 percent during that time The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today far



1




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know
This lesserknown greenhouse gas will make or break a "decisive decade" for climate change By Rebecca Leber @rebleber , 0pm EDT Share this story Greenhouse gas emissions Germany 'set for biggest rise in greenhouse gases for 30 years' Increase means country will slip back fromHuman activities are responsible for almost all of the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere over the last 150 years 1 The largest source of greenhouse gas emissions from human activities in the United States is from burning fossil fuels for electricity, heat, and transportation
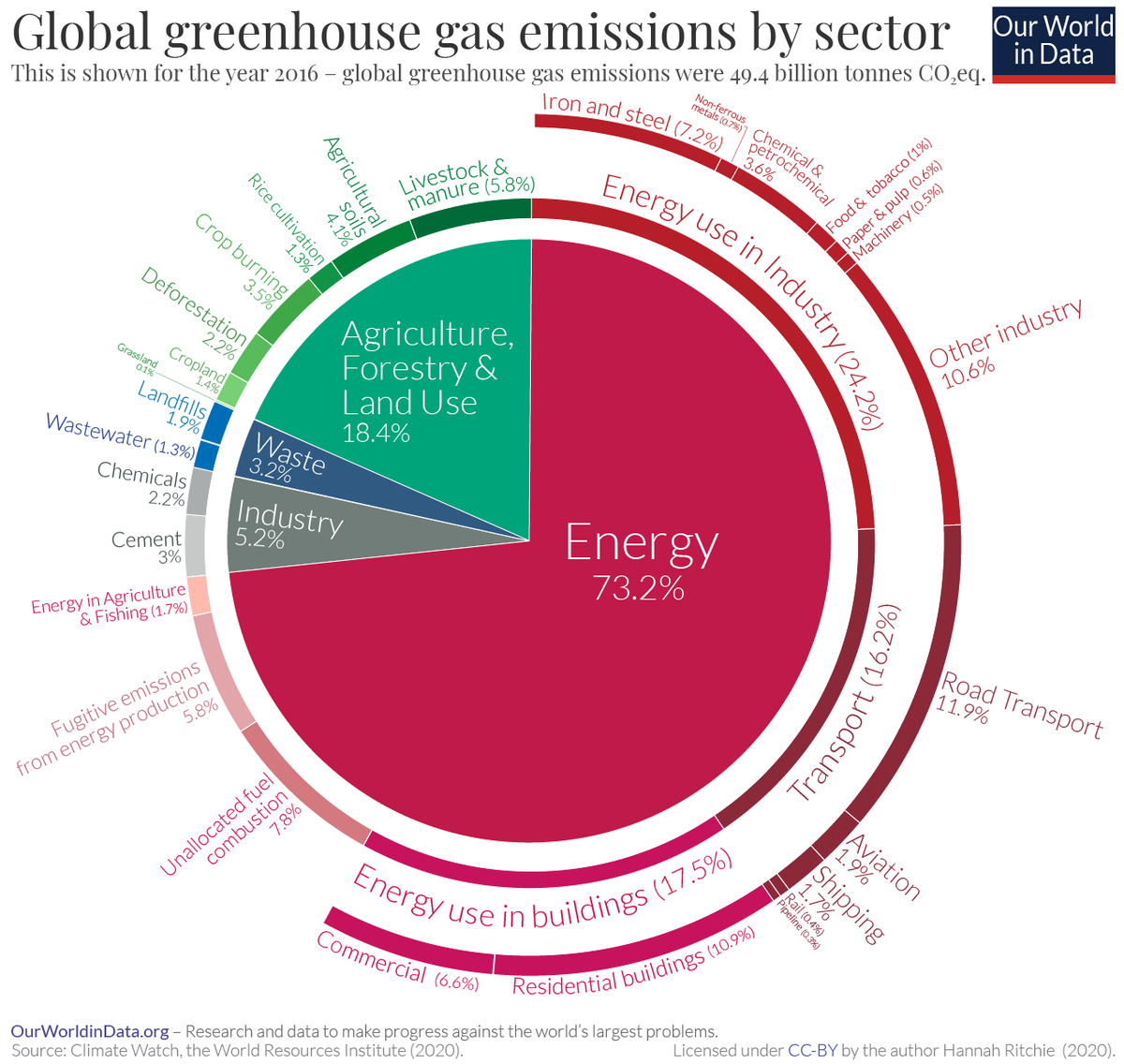



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
Greenhouse gas emissions are greenhouse gases vented to the Earth's atmosphere because of humans the greenhouse effect of their 50 billion tons a year causes climate changeMost is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels coal, oil, and natural gas The largest polluters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many stateowned by OPEC and RussiaFluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6Greenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3) Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization
Now, over a century later, the mention of greenhouse gas usually evokes thoughts of carbon dioxide (CO 2)That's mainly because changes in the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere have been linked to the warming of the atmosphere over this past century CO 2 is an important greenhouse gas, and along with water vapor, keeps the Earth warm enough to support life as we know it
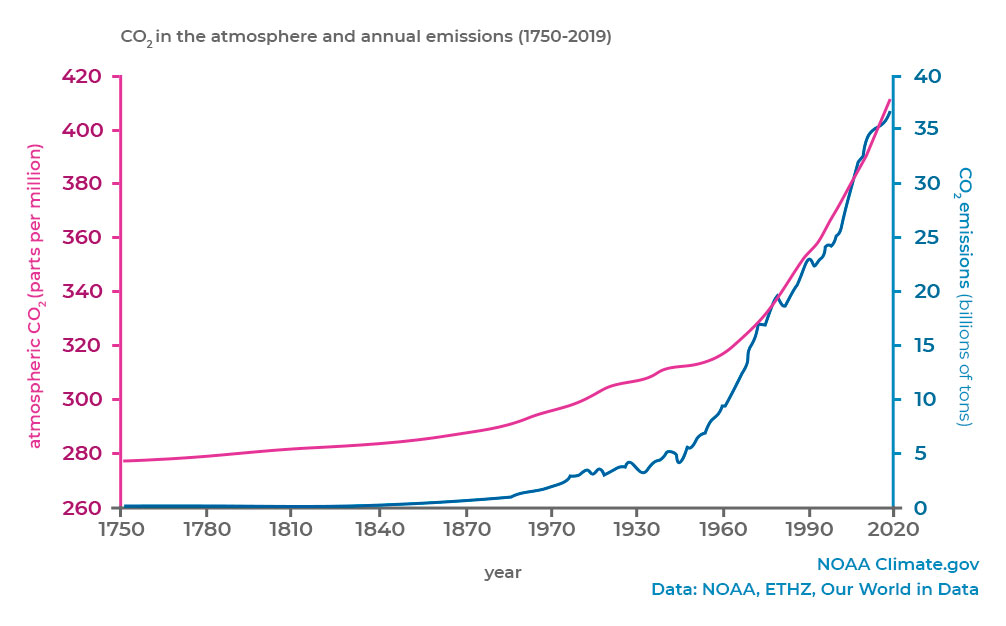



Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Agriculture Proterra Foundation
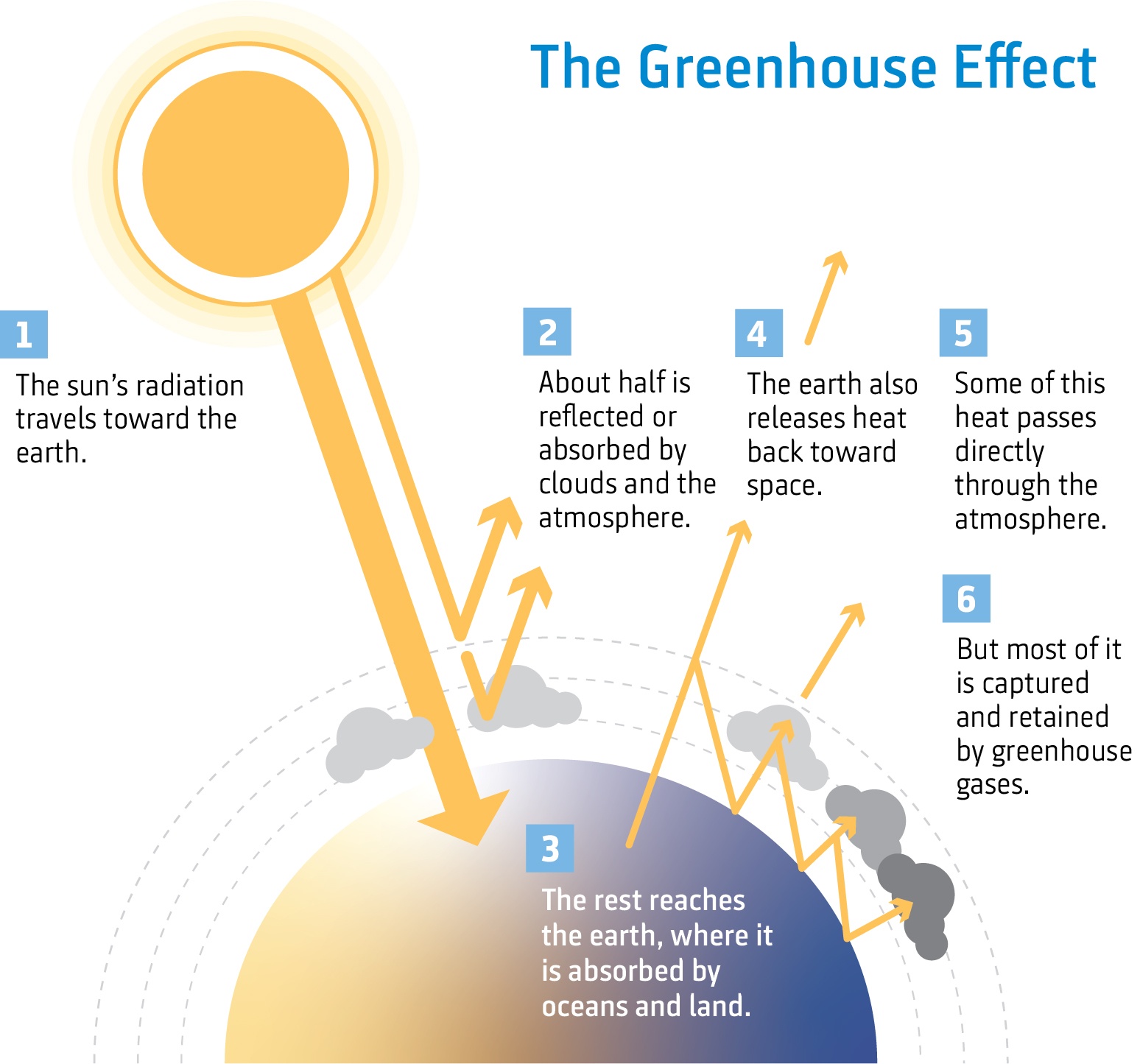



Climate Change The Science Niwa




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Santa Fe City Of Santa Fe New Mexico
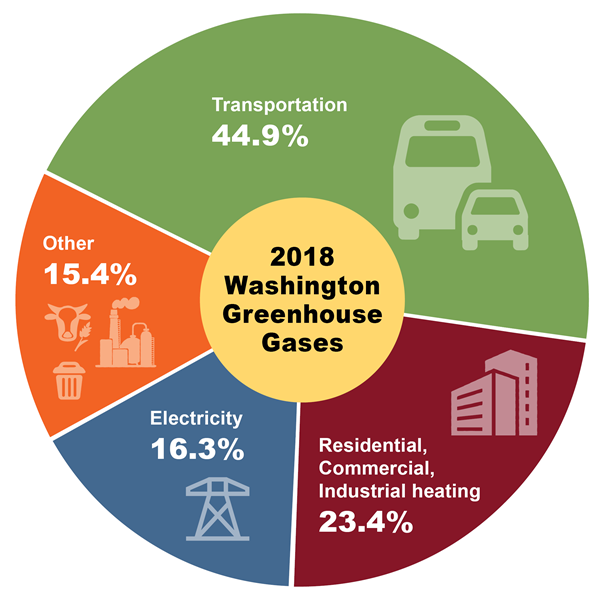



18 Data Washington State Department Of Ecology




How Trump Is Ensuring That Greenhouse Gas Emissions Will Rise The New York Times
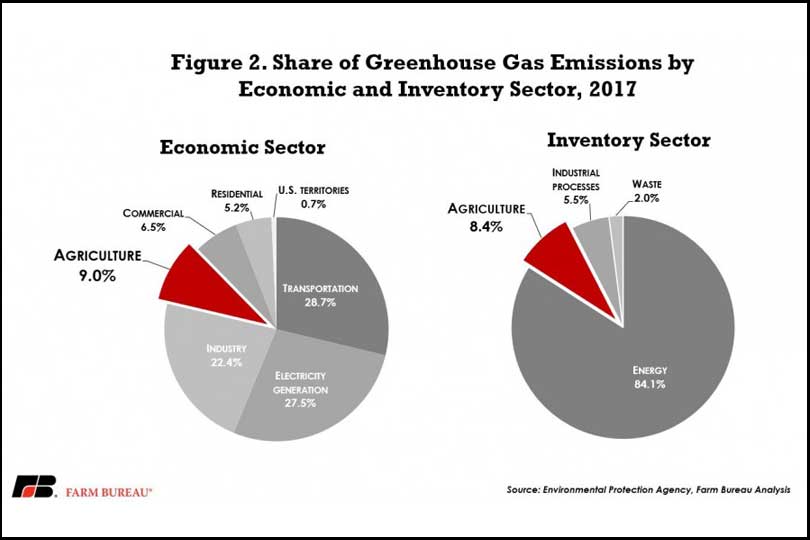



Report Clears Air On Greenhouse Gas Emissions For Cattle Texas Farm Bureau



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming




Greenhouse Gases 101 Ben Jerry S




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research
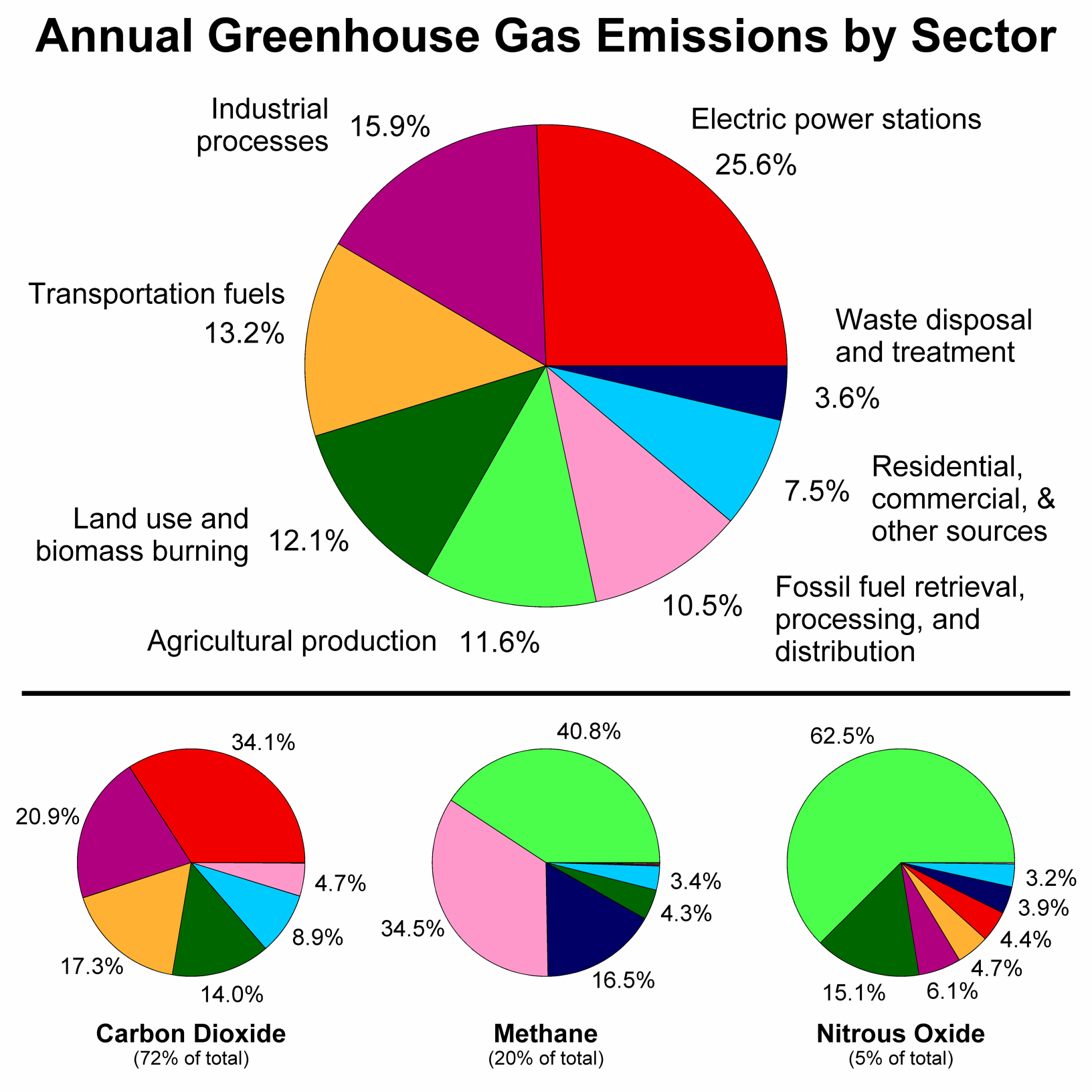



File Greenhouse Gas By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons




Removing Harmful Greenhouse Gases From The Air Using Energy From Plants Frontiers For Young Minds




Greenhouse Gases World Meteorological Organization
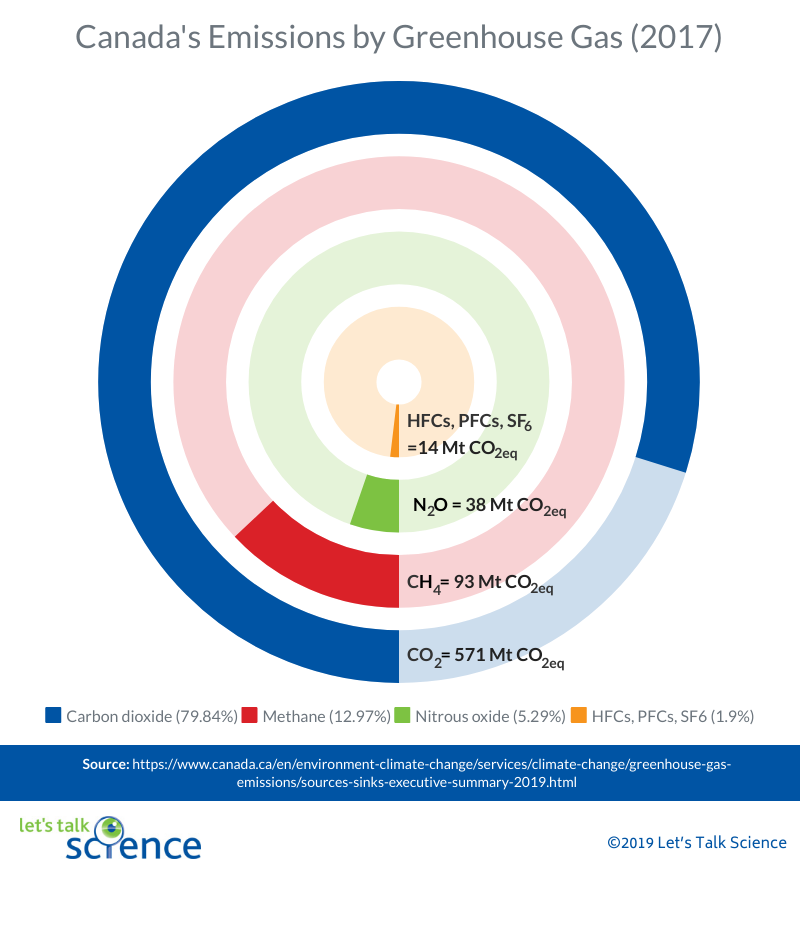



What Are Greenhouse Gases Let S Talk Science




Banning The Super Greenhouse Gas Environment All Topics From Climate Change To Conservation Dw 17 10 16




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




Pork Production And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Pork Information Gateway




With Emissions On The Rise Oregon Falls Well Short Of Greenhouse Gas Reduction Goals Oregonlive Com
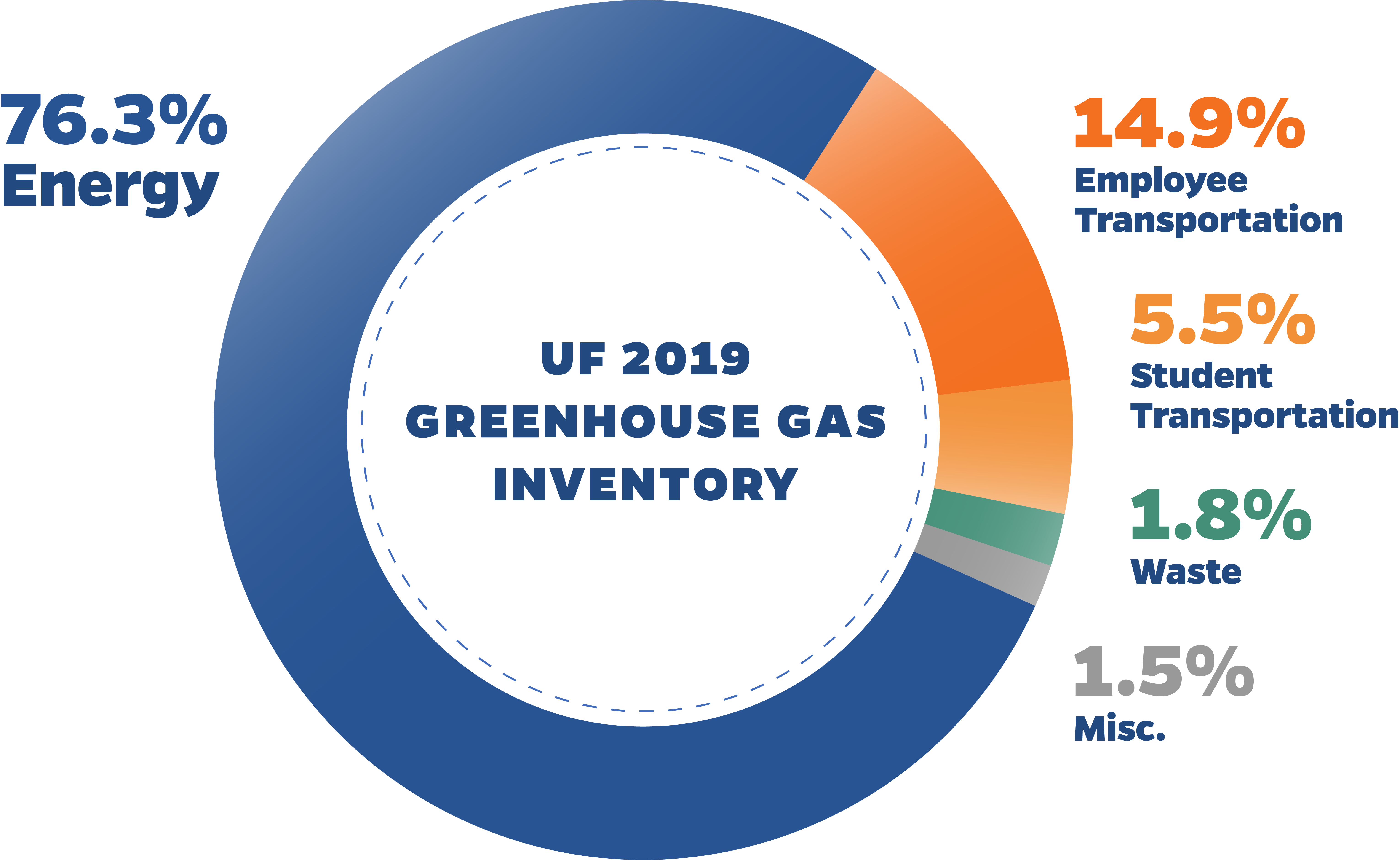



Uf Greenhouse Gas Inventory Sustainability Sustainability University Of Florida Business Affairs University Of Florida




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament



Greenhouse Gases



Small Increase In Eu S Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions In 17 With Transport Emissions Up For The Fourth Consecutive Year European Environment Agency
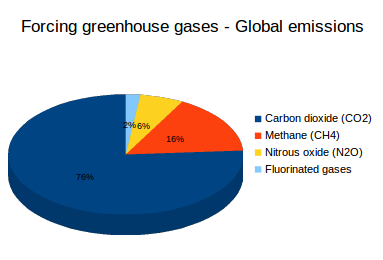



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact




What Does The Spike In U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Mean




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Plunge In Response To Coronavirus Pandemic Inside Climate News




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Gas Neutral Europe And The Role Of Geology Geoera




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids



Progress To Greenhouse Gas Emission Targets European Environment Agency




Emissions Of The Powerful Greenhouse Gas Sf6 Are Rising Rapidly World Economic Forum




Matt Canavan Shrugs Off Australia S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Increase Energy The Guardian




What S The Deal With Greenhouse Gases Emissions And The Environment Futurelearn



1
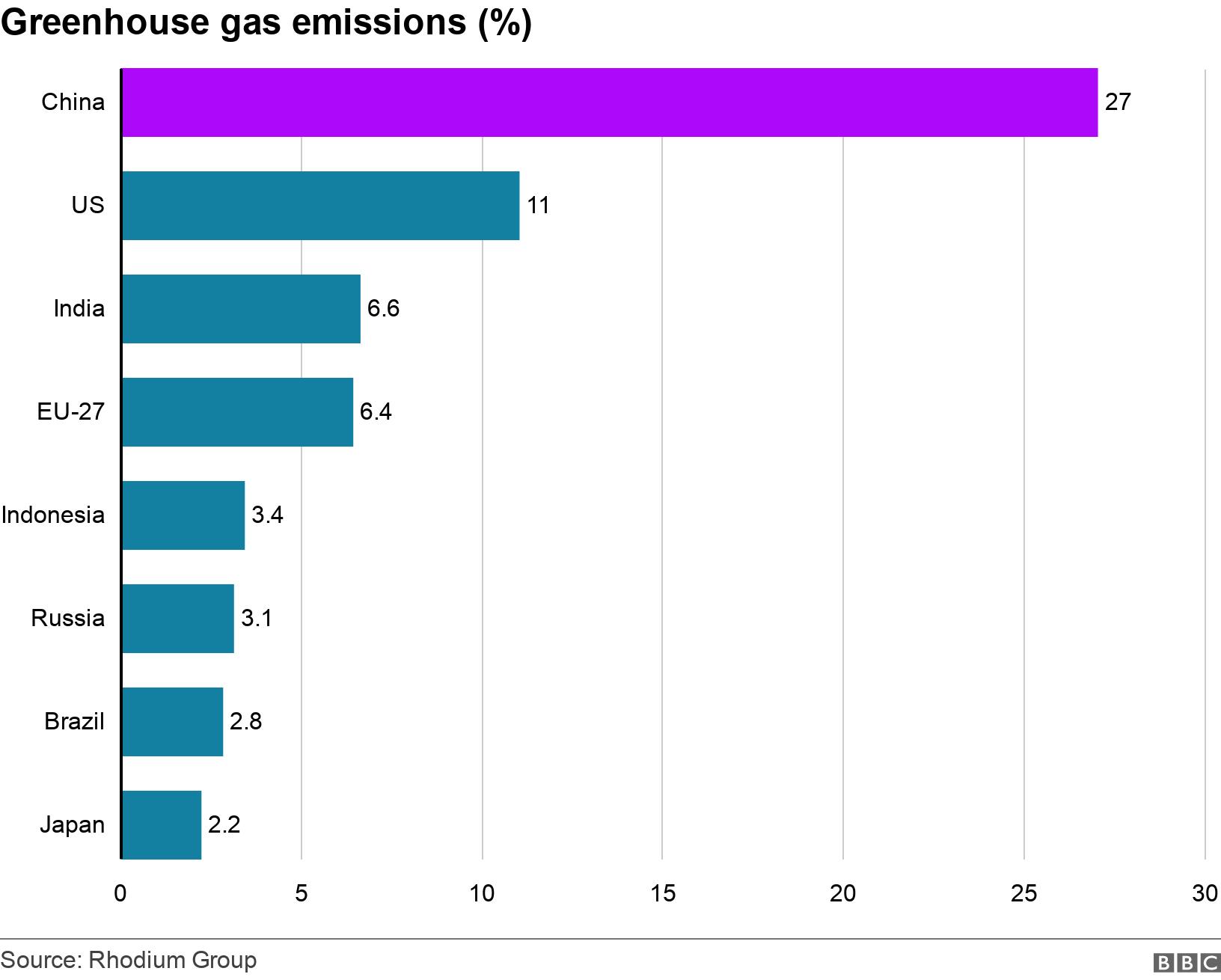



Report China Emissions Exceed All Developed Nations Combined c News
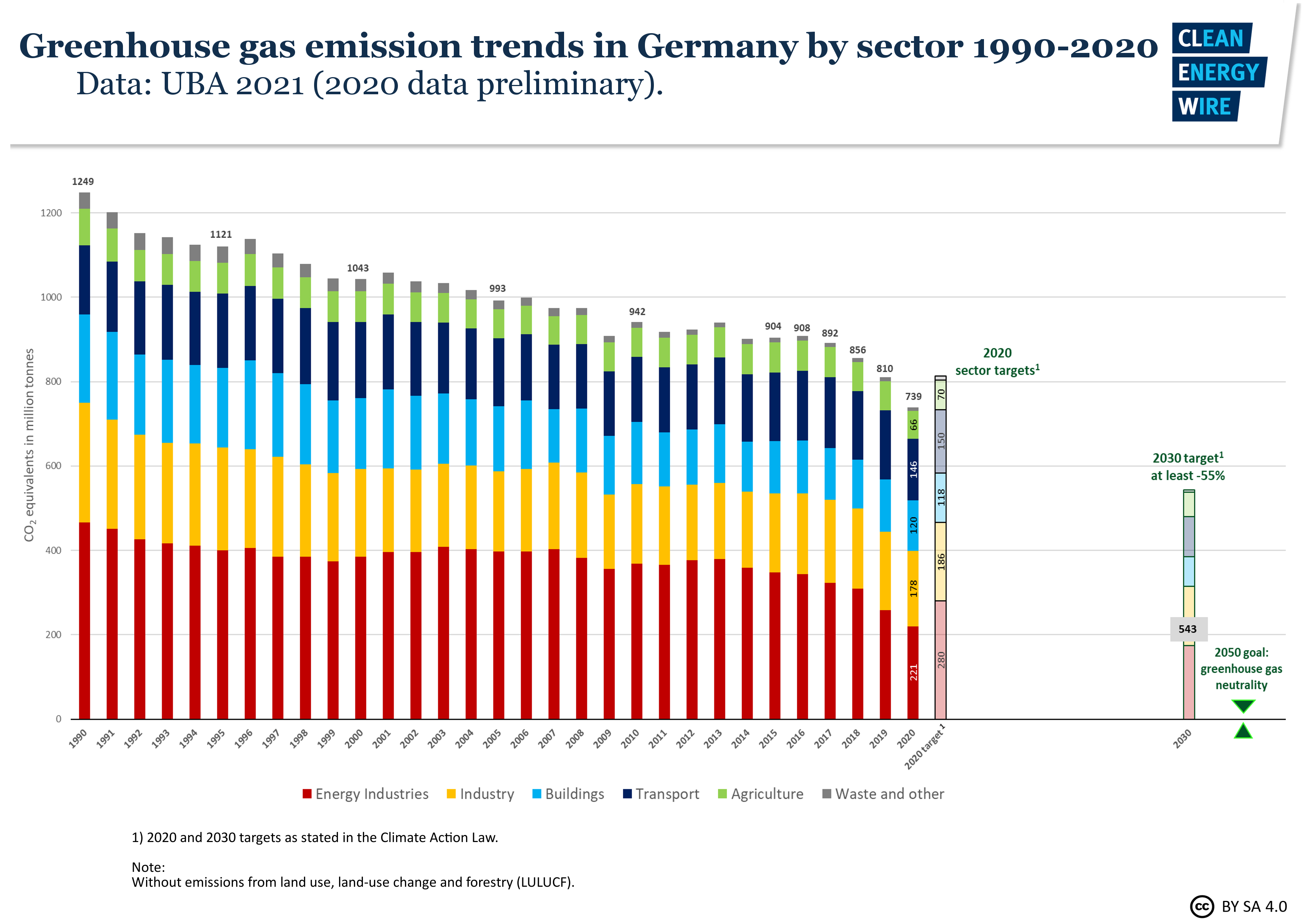



Germany Sees Record Greenhouse Gas Emission Fall Due To Pandemic Renewables Clean Energy Wire




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases



1




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
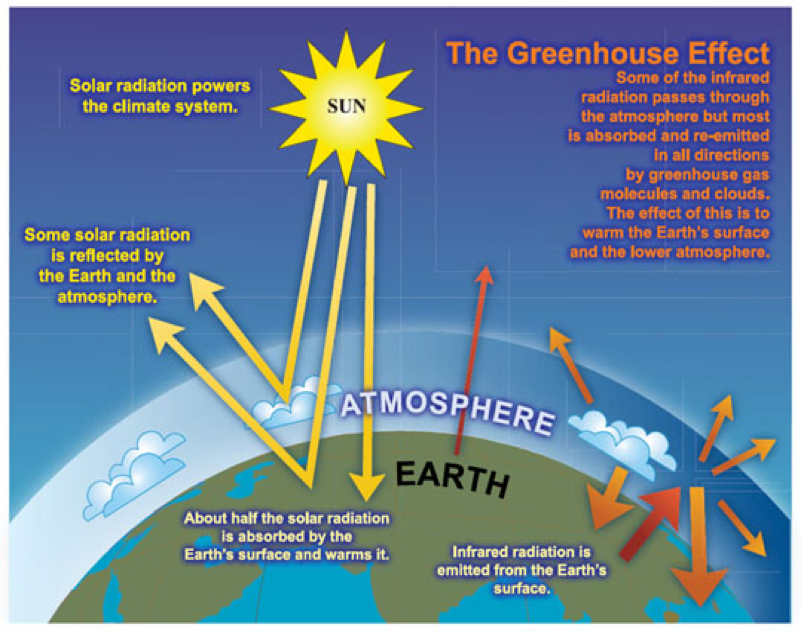



Greenhouse Gas Reduction




What Are Greenhouse Gases And Why We Need To Worry About Them A Simple Explainer



Greenhouse Gases
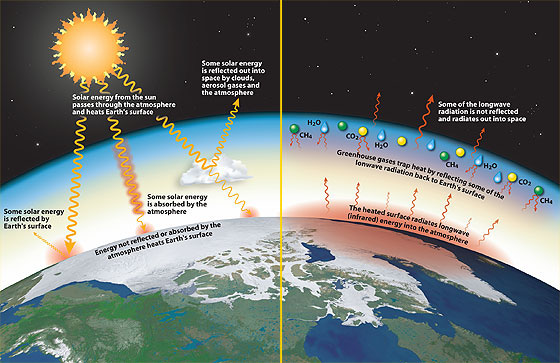



Too Much Of A Good Thing
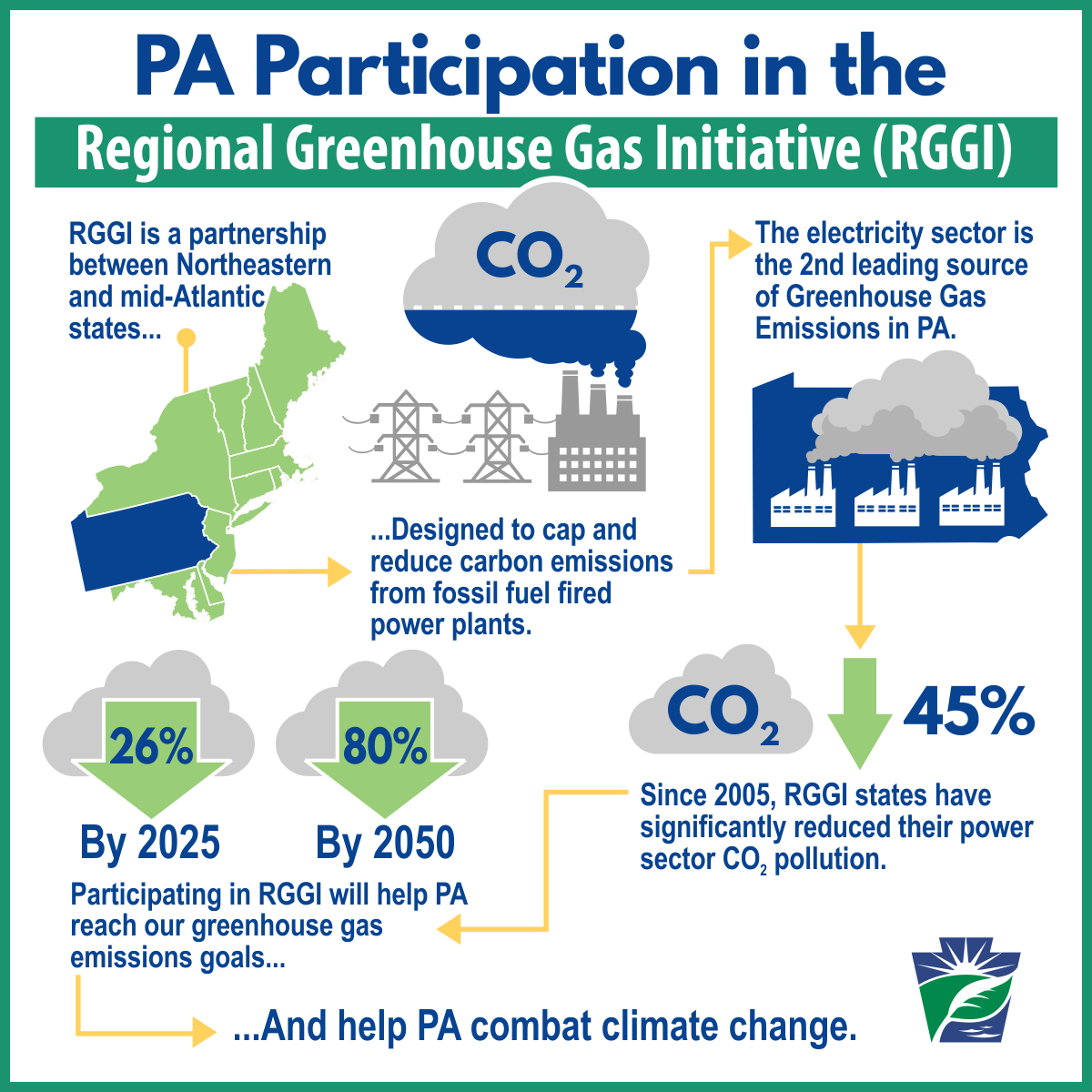



Rggi
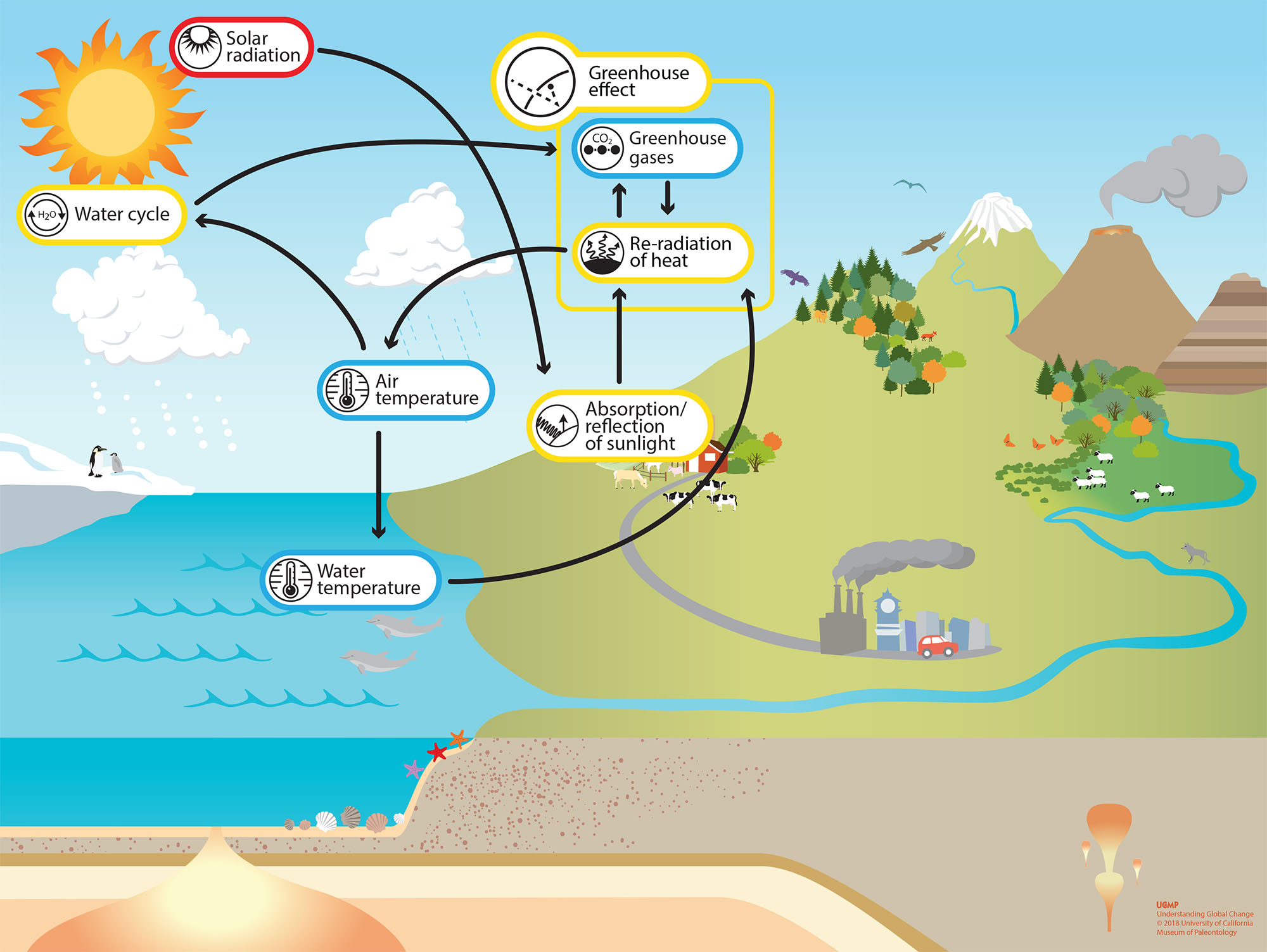



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change




World Greenhouse Gas Levels Made Unprecedented Leap In 16




Saudi Arabia Greenhouse Gas Emissions Have Increased By 225 Since 1990 Climate Scorecard




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Uk Fell 3 In 18 Official Figures Show Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Guardian




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
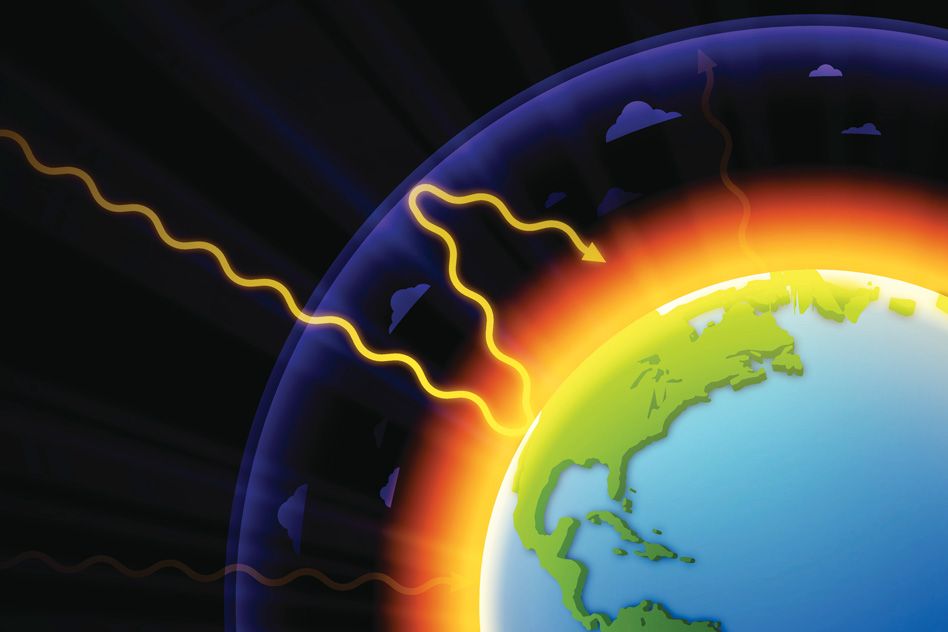




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Public Health Benefits Of Strategies To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions Health Implications Of Short Lived Greenhouse Pollutants The Lancet




They Just Kept On Rising Data Reveals Alarming Greenhouse Gas Increase




Minnesota Falls Further Away From Greenhouse Gas Reduction Goals Star Tribune



Chart China Beats U S Europe In Combined Greenhouse Gases Statista
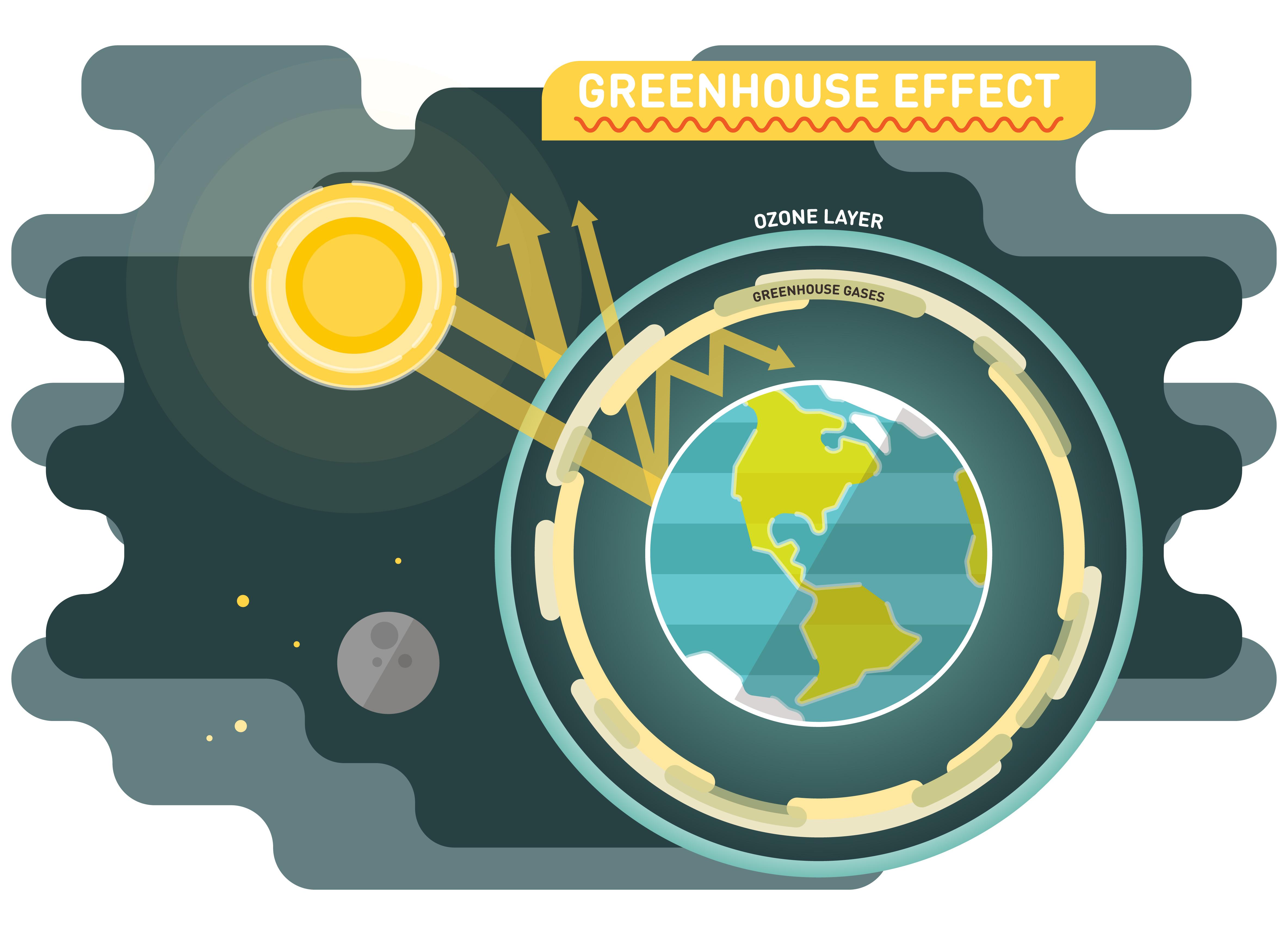



Why The Greenhouse Effect Is Important How It Affects The Climate




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
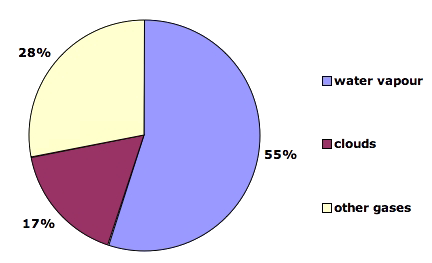



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Definition Solution Facts




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Wmo Greenhouse Gas Bulletin The State Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Based On Global Observations Through 18 No 15 25 November 19 World Reliefweb




Some Greenhouse Gases Are Stronger Than Others Ucar Center For Science Education




Greenhouse Gases What Is Warming Up Our Earth




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




The Two Degree Difference Us Greenhouse Gas Emissions Down 10 In
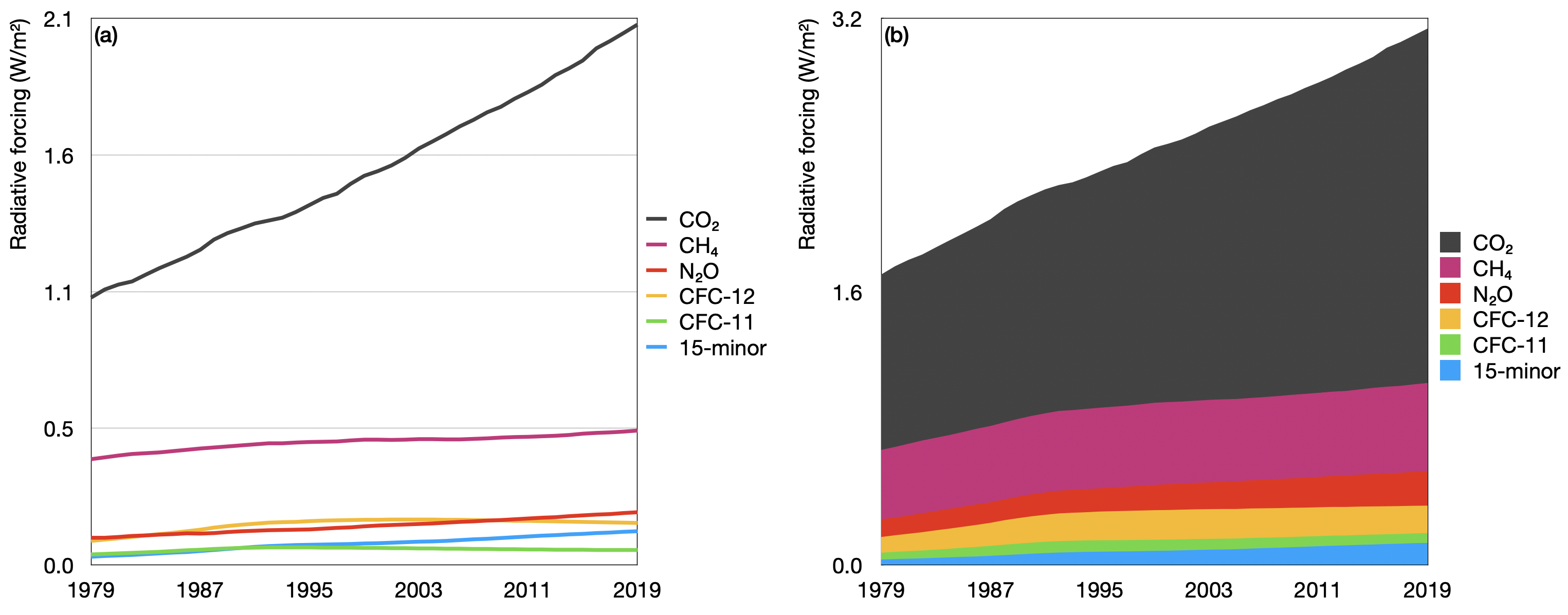



Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus




File Greenhouse Effect Svg Wikimedia Commons
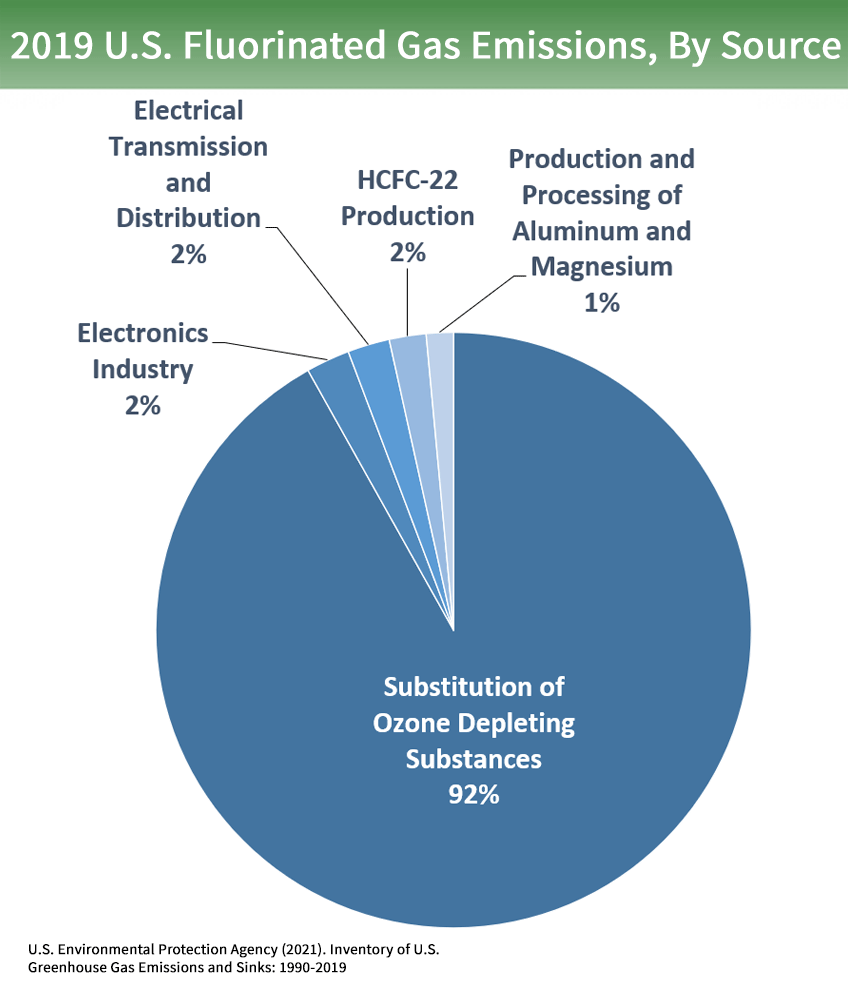



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿